Does double-blind peer review impact gender authorship trends? An evaluation of two leading neurosurgical journals from 2010 to 2019
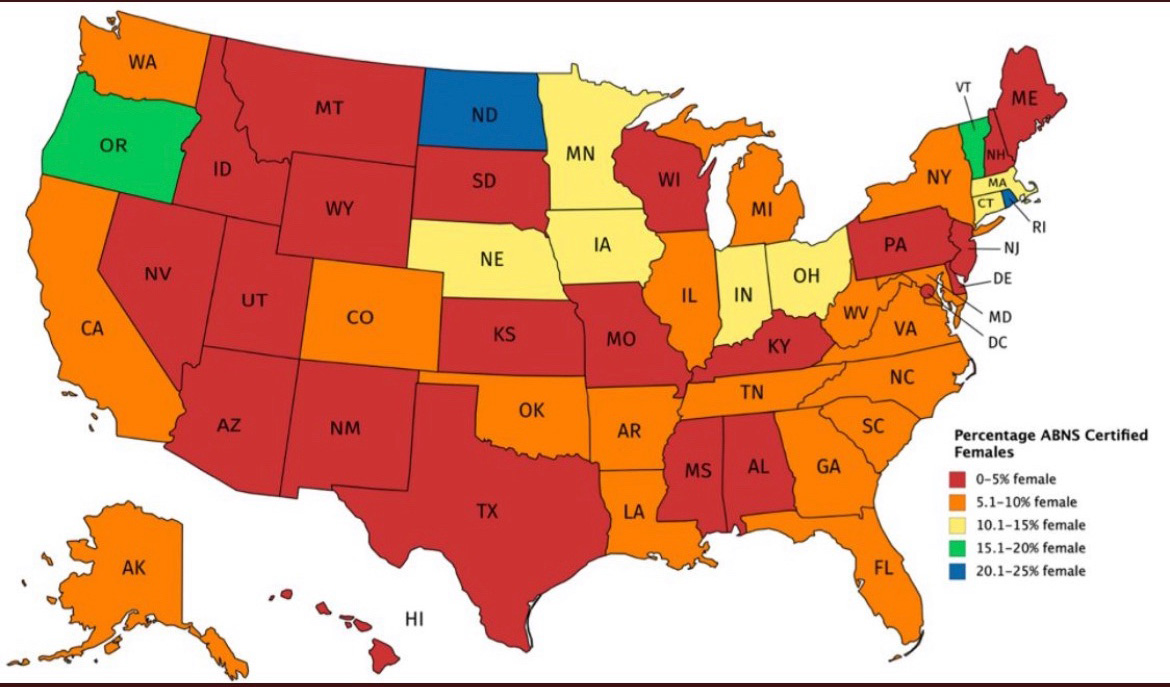
Article reveals the State of Rhode Island has one of the highest percentages of ABNS certified women in neurosurgery in the country.
Article Objective: “Publications are key for advancement within academia. Although women are underrepresented in academic neurosurgery, the rates of women entering residency, achieving board certification, and publishing papers are increasing. The goal of this study was to assess the current status of women in academic neurosurgery publications. Specifically, this study sought to 1) survey female authorship rates in the Journal of Neurosurgery (JNS [not including JNS: Spine or JNS: Pediatrics]) and Neurosurgery from 2010 to 2019; 2) analyze whether double-blind peer review (started in Neurosurgery in 2011) altered female authorship rates relative to single-blind review (JNS); and 3) evaluate how female authorship rates compared with the number of women entering neurosurgery residency and obtaining neurosurgery board certification.”
Read Full Article: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/